Please cite! If you use QSB databse for research, please cite the following paper:
Ying Jin, Wenkang Chen, Jie Hu, Jinfeng Wang*, Hongqiang Ren. Constructions of quorum sensing signaling network for activated sludge microbial community [J]. ISME Communications, 2024, 4(1), ycae018.
Quorum sensing (QS) is widely recognized as a key process in bacterial communication that coordinates group behavior in the bacterial world. Quorum sensing is a common phenomenon in bioaggregates such as activated sludge, biofilm and granular sludge. It is of great significance for wastewater treatment to understand the regulation behavior between quorum sensing and microorganisms.
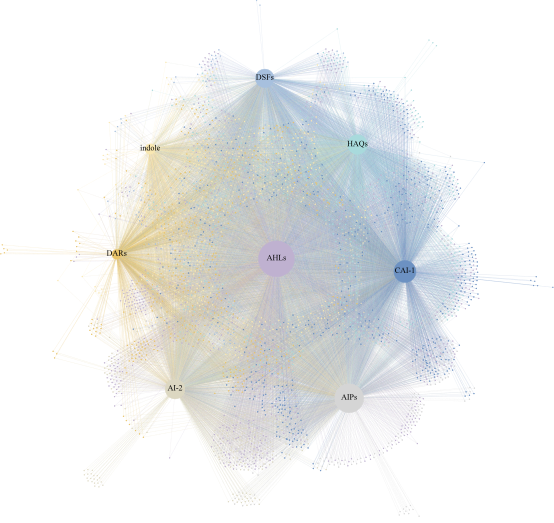
QSB database is a comprehensive and accurate database of activated sludge quorum sensing microbial communities, containing 193306 quorum sensing related protein entries from 4167 activated sludge microbial species. These entries cover a variety of quorum sensing signaling systems, These include AHLs (N-acyl homoserine lactones), AI-2 (autoinducer-2), HAQs (4-hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines), and DSFs (diffusible signal) factors), indole, CAI-1 (cholerae autoincer 1), DARs (diketopiperazines), and AIPs (autoinducing peptides). Starting from 192 QS entries collected from SigMol and Quorumpeps databases and their homologues in the reference proteomes of 4228 microbial species identified in the MiDAS 4 database, the database combined with random forest, four classifiers developed by random forest (RF), K-nearest neighbor (KNN), support vector machine (SVM), and deep neural network (DNN) machine learning algorithms, as well as further protein annotation, functional analysis, and homology modeling to mine more potential QS protein entries.
With the help of QSB database, we can search the intraspecific and interspecific interactions of activated sludge microbial communities based on quorum sensing communication, and further construct and analyze the complex quorum sensing communication network of activated sludge microbial communities, so AS to enhance our understanding of quorum sensing communication of activated sludge microbial communities. This will help us to better understand and utilize the role of quorum sensing microorganisms in wastewater treatment.
